Parts of Texas were as cold as Mars during recent big freeze, as rolling blackouts visible from space
When Texas was blasted by a once-in-a-century cold snap, as a cold air mass extended south from Canada and across the US, the state’s energy infrastructure failed, causing rolling blackouts that were visible from space.
A combination of snow and unseasonably cold temperatures resulted in numerous equipment failures which severely hampered power generation and supply issues across the Lone Star state. Weather satellites, calibrated to the state’s more temperate climate, were so confused they mistook the frozen ground for clouds.
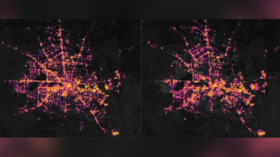
Also on rt.com As Texans struggle to get food & water, record-breaking freeze is so cold it’s confusing weather satellitesNASA's Earth Observatory captured the effect of the subsequent rolling blackouts across the greater Houston area in images captured on February 7, the day before the Arctic blast hit, and then on February 16, when large areas of the city plunged into icy darkness.

Nighttime light data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite, or VIIRS, is laid atop Landsat imagery which captures the city's infrastructure, providing more clarity to the image and showcasing the full extent of the blackouts.
NASA is constantly monitoring nocturnal light emissions across the globe as part of its Black Marble program which aims to further humanity’s understanding of light pollution, wildfires, natural disasters and recovery, as well as the extent of human settlements and their associated energy infrastructures.
Among the US space agency's plethora of satellite data, it found that, at one point during the recent big freeze in Texas, the city of Dallas reached -16 Celcius (four degrees Fahrenheit) which is comparable with temperatures recorded by the Curiosity Rover at the Gale Crater on Mars.
Also on rt.com Four board members of Texas grid operator RESIGN over blackouts during deadly winter stormThink your friends would be interested? Share this story!













