World population set to shrink rapidly triggering ‘radical power shift’, warns new bombshell report

While predictions of a potentially catastrophic population explosion have abounded for years, new research suggests a major impending contraction by 2100, at which point the elderly will outnumber the young.
The Lancet has just published its ‘Global Burden of Disease Study’ which cites an accelerated decline in fertility rates across the developed world in coming decades. The report predicts that the world population will peak in 2064 at 9.7 billion people, before dropping precipitously to 8.8 billion by 2100.
According to the researchers, the elderly will account for a larger percentage of the global population, with octogenarians projected to outnumber toddlers under five by two-to-one by the turn of the next century.
Also on rt.com Coronavirus 2.0 may be up to NINE TIMES more contagious … but that may be cause for celebrationThe populations of some 23 countries including Japan, Thailand, Italy, and Spain could contract by at least 50 percent, while 183 of 195 countries included in the research would have fertility rates below the replacement level of 2.1 births.
On the one hand, China and 34 other countries are expected to witness a population decline of over 25 percent, but on the other, both Latvia and El Salvador will experience population declines of over 75 percent.
The report cites contraception access and improved education of girls and women as the primary catalysts which will “hasten declines in fertility and slow population growth.”
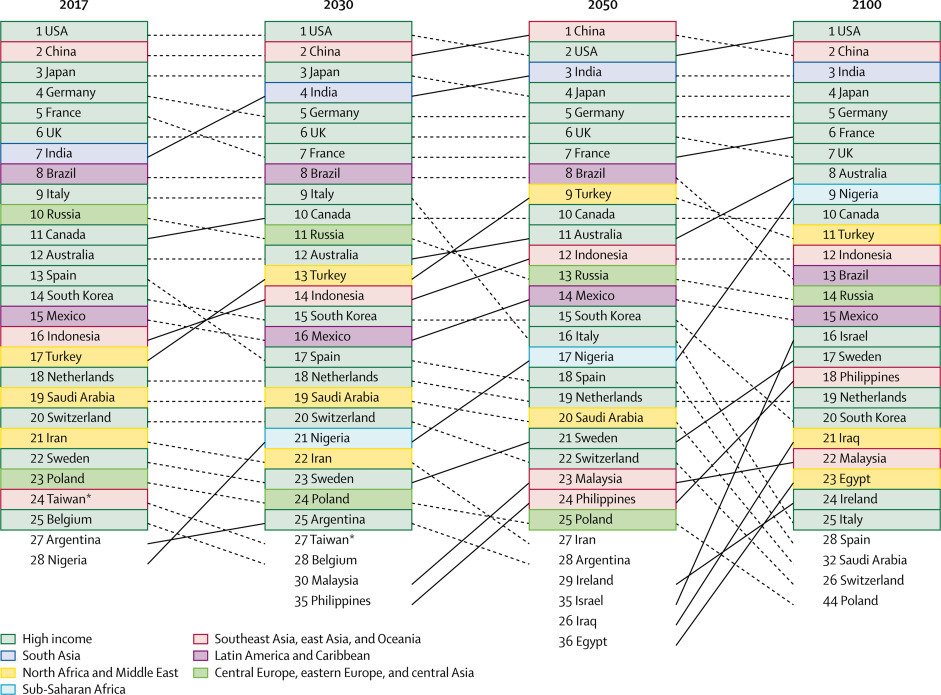
“Continued global population growth through the century is no longer the most likely trajectory for the world’s population,” said Dr. Christopher Murray, who led the study, adding that governments around the world need to “start rethinking their policies on migration, work forces and economic development.”
The report envisages major declines in the working-age populations in China and India, emerging economic powers at present that would likely fade in influence were this demographic shift to play out as predicted. The US could re-emerge as a world-leading economic power by 2098 after a dip in both population and economic influence.
The study suggested liberal immigration policies as a means to mitigate population decline and bolster economic growth, especially for industrialized countries like the US, Australia, and Canada.
Meanwhile, sub-Saharan Africa will likely experience up to a three-fold population explosion, due to a combined drop in death rates and concurrent increase in the number of women reaching child-bearing age. According to the study’s authors, Niger could see 765 percent growth, Chad 710 percent growth, South Sudan 594 percent, and Mali 321 percent.
PTI News (Decline in fertility will see global population shrink, triggering radical shifts in economic power - report) has been published on PTI News - https://t.co/SUoauWrafapic.twitter.com/GaaC5u5Vy4
— SiasatToday (@SiasatToday) July 15, 2020
For this reason, Africa would likely overshadow Asia as the world’s most-populated region by the turn of the next century.
The study also predicts the emergence of a far more multipolar world with India and Nigeria expected to join the US and China as the dominant global powers, while more African and Arab countries would take the reins as global economic leaders.
“It offers a vision for radical shifts in geopolitical power, challenges myths about immigration, and underlines the importance of protecting and strengthening the sexual and reproductive rights of women. The 21st century will see a revolution in the story of our human civilisation,” Dr. Richard Horton, editor in chief of the Lancet, said.
Think your friends would be interested? Share this story!













